Setting Up SolidX
System Requirements
To try out SolidX on your local machine, ensure you have the following prerequisites installed.
Prerequisites
- Node.js: Latest Active LTS
- npm: Included with Node.js
- Docker: Latest stable version
Supported Systems
- macOS
- Linux
System Requirements
- CPU: 2 cores
- Memory:
- Minimum: 4 GB RAM
- Recommended: 8 GB RAM (for a smoother experience)
- Disk: 5 GB free space
SolidX itself is lightweight and does not require significant memory.
The requirements above are intended for a smooth local development experience, especially when running development tools and containers.
Database Setup
If you already have a PostgreSQL database installed and running on your system, you can skip this section and proceed directly to SolidX Scaffolding Script. Just make sure you have your database connection details (host, port, username, password, and database name) ready for the scaffolding step.
SolidX requires a relational database to store application data / metadata. Currently supported databases include PostgreSQL and MSSQL.
We will be using PostgreSQL for this tutorial.
Below are instructions to set up PostgreSQL locally using Docker, which provides an isolated and easy-to-manage environment for your database.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, Docker must be installed and running on your system.
- macOS / Windows: Install Docker Desktop
- Ubuntu / Linux: Install Docker Engine
After installation, ensure Docker is running and verify it by executing:
docker --version
# Expected output (version may vary):
# Docker version 27.5.1, build 9f9e405
Installing PostgreSQL
We will be installing PostgreSQL 17 using the official Docker image.
Step 1: Pull PostgreSQL 17 Image
Pull the official PostgreSQL 17 image from Docker Hub.
docker pull postgres:17
Step 2: Run the PostgreSQL Container
Run PostgreSQL with a predefined username, password, database name, port binding, and persistent storage using the postgres:17 image.
docker run -d \
--name SolidX_DB \
-e POSTGRES_USER=solidx_app_user \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=strongpassword \
-e POSTGRES_DB=solidx_app_db \
-p 5432:5432 \
-v solidx_pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data \
postgres:17
Above step initializes an empty database with the specified credentials and configuration and starts the PostgreSQL server in a Docker container.
PostgreSQL data will be stored in the Docker volume solidx_pgdata which is specified using the -v flag. This is useful for the following reasons:
- Data persists across container restarts
- Removing the container does not delete the data
- Removing the volume deletes all stored data
Step 3: Verify the Container Is Running
Check the list of running containers.
docker ps
# Expected output should include a container named "SolidX_DB" with the postgres:17 image
#CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
#3aabaa074778 postgres:17 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 11 seconds ago Up 9 seconds 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp SolidX_DB
Step 4: Connect to PostgreSQL
Use the following details in your application or database client e.g pgAdmin, DBeaver, or any PostgreSQL client.
- Host: localhost
- Port: 5432
- Username: solidx_app_user
- Password: strongpassword
- Database: solidx_app_db
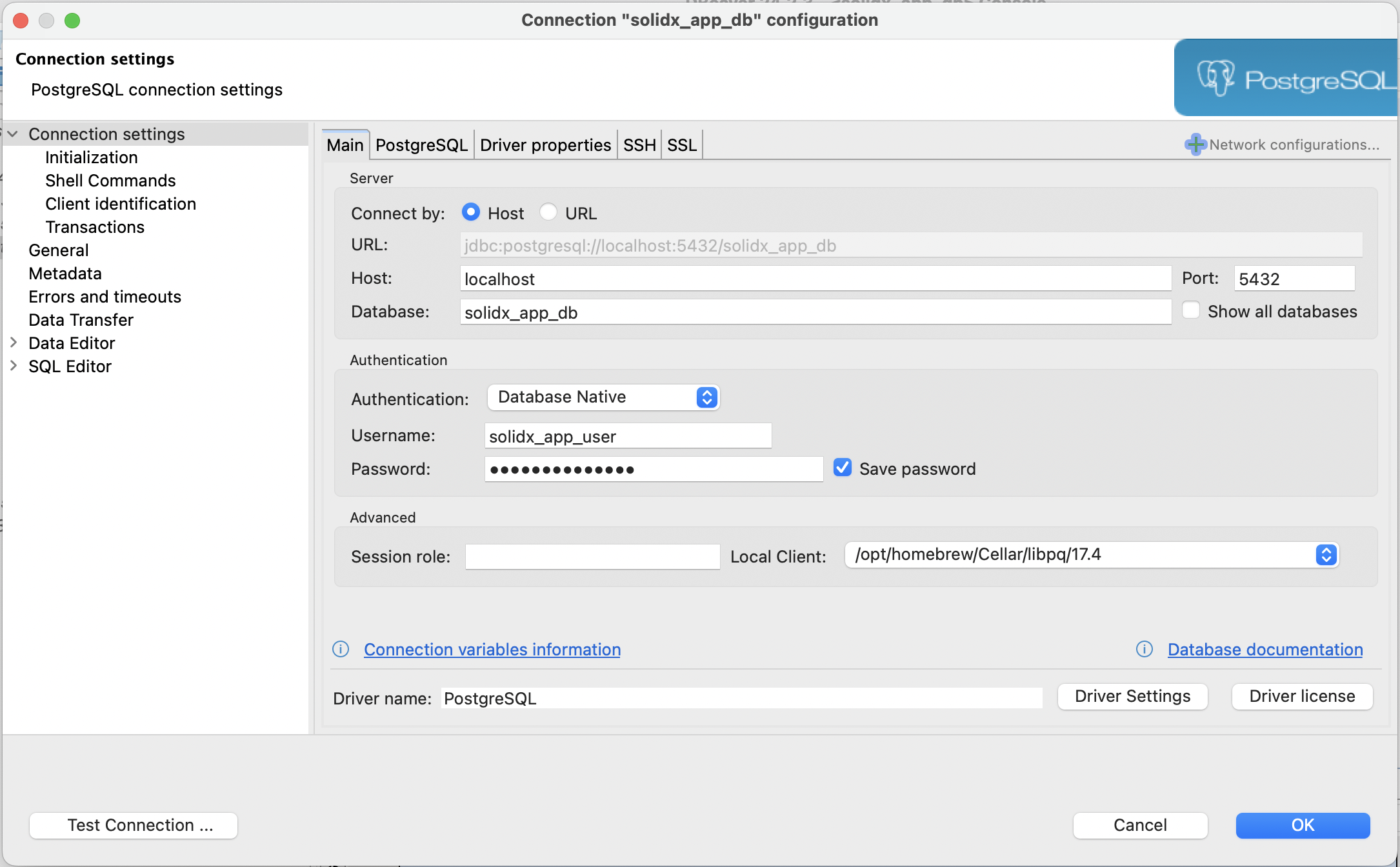
Screenshot showing how to connect to the running PostgreSQL server using DBeaver
Step 5: Managing the Container
Stop the PostgreSQL container.
docker stop SolidX_DB
Start the PostgreSQL container again.
docker start SolidX_DB
- Running PostgreSQL using Docker is recommended for local development and testing environments.
- For production deployments, it is advised to use a managed PostgreSQL service or a carefully maintained database setup with proper backups, monitoring, and high availability.
- If you want to reset the database and start afresh, you can remove the Docker volume storing the data.
# Stop the container first
docker stop SolidX_DB
# Remove the container
docker rm SolidX_DB
# Then remove the volume
# Warning: This deletes all data in the database!
docker volume rm solidx_pgdata
- Then you can re-run the container using the command in Step 2 to create a fresh database.
SolidX Scaffolding Script
SolidX applications are installed and initialized exclusively using the official scaffolding script.
To create a new SolidX application, run:
npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest create-app
npx, bundled with Node.js, runs packages directly without requiring a global install — ensuring you always use the latest version ofsolidctl.
What create-app Does
Launches an interactive setup that produces a fully working, end-to-end application.
Specifically, it:
-
Bootstraps the backend (APIs)
- Sets up a fully functional backend application
- Exposes a complete set of REST APIs
- Generates Swagger / OpenAPI documentation for all APIs
-
Bootstraps the frontend (Admin Panel)
- Sets up a ready-to-use admin panel
- Integrates the frontend with backend REST APIs out of the box
-
Applies correct SolidX project structure and conventions
- Backend and frontend projects follow SolidX-defined project structures and best practices
- Configuration, environment files, and scripts are wired correctly
-
Other Control Plane CLI Commands
- npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest seed — Seed the database with canonical models, settings, and system users from configuration files.
- npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest build — Builds the backend and updates the CLI to point to the latest codebase.
- npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest upgrade — Upgrade Solid dependencies belonging to the
@solidxaiorganization in thesolid-apiandsolid-uiprojects to their latest published versions.
See the full solidctl Command Reference for details on all available commands.
Prerequisites
Ensure the following are available before running the starter script.
Node.js (Required)
- Required: Node.js 22 or later
- Recommended: Latest LTS version (via nvm or from https://nodejs.org)
Verify installation:
node -v
# Expected output (version may vary):
# v22.0.0
Recommended: Node Version Manager (nvm)
We recommend installing Node.js using nvm to easily manage and switch Node versions, avoid system conflicts, and ensure compatibility with SolidX.
Install nvm using the official instructions:
https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm
Once installed, set up the required Node version:
nvm install 22
nvm use 22
# Verify the correct version is active
# node -v
npm
npm is bundled with Node.js and is used by the starter script.
Verify installation:
npm -v
# Expected output (version may vary):
# 10.0.0
Terminal & Internet Access
- Access to a command-line terminal (macOS, Linux, or Windows)
- Active internet connection (required to download and run the starter)
The next section walks you through the create-app command step by step, including each prompt and screenshots for reference.
Bootstrapping Your Application
Run npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest create-app as described above and follow the prompts below to configure your application:
Backend Configuration Prompts
- Project Name: Enter a name for your SolidX application.
- Example:
school-fees-portal - Default:
my-solid-app
- Backend API Port: Enter the port for the backend API server.
- Default:
3000
- Database: Select the database for your application.
- Options:
PostgreSQL,MSSQL - Default:
PostgreSQL
- Database Host: Enter the database host address.
- Default:
localhost
- Database Port: Enter the database port.
- Default for PostgreSQL:
5432
- Database Name: Enter the database name.
- Default:
solidx_app_db
- Database Username: Enter the database username.
- Default:
solidx_app_user
- Database Password: Enter the database password.
- Default:
strongpassword
- Sync Database Schema: Choose whether to automatically synchronize the database schema.
- Options:
Yes,No - Default:
Yes
This option is not recommended for production environments, since it modifies the database schema automatically. It is advisable to manage database migrations manually in production.
Frontend Configuration Prompts
- Admin Panel Port: Enter the port for the admin panel frontend.
- Default:
3001
SolidX Bootstrapping in Action

Verbose logging — Add --verbose for detailed output when diagnosing failures:
npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest create-app --verbose
Package resolution errors — Clear the npm cache and retry:
npm cache clean --force
npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest create-app
Bootstrapping Application Metadata
SolidX requires foundational metadata: system models, roles, users, email/SMS templates, dashboards, and lists of values.
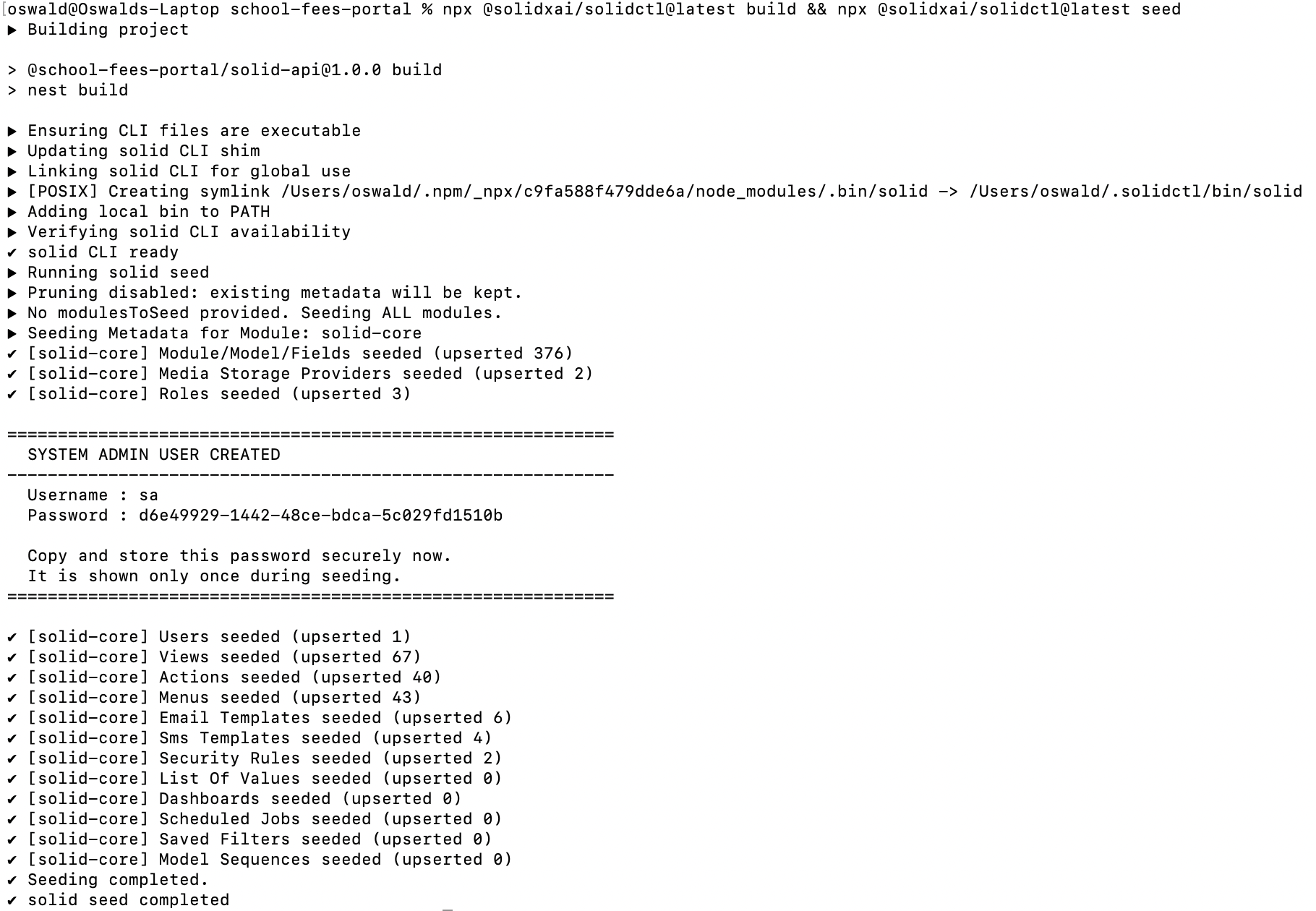
The npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest seed command automates this process by populating the database with all these essentials, making the application ready for immediate use.
To seed the database, navigate to the project root directory and run:
cd school-fees-portal
npx @solidxai/solidctl@latest seed
This command reads predefined JSON files containing the necessary metadata for a SolidX application and populates the database accordingly.
The seed process also creates an super admin user, if one does not already exist. The credentials for this user are displayed in the terminal after seeding is complete.
Seeding in Action
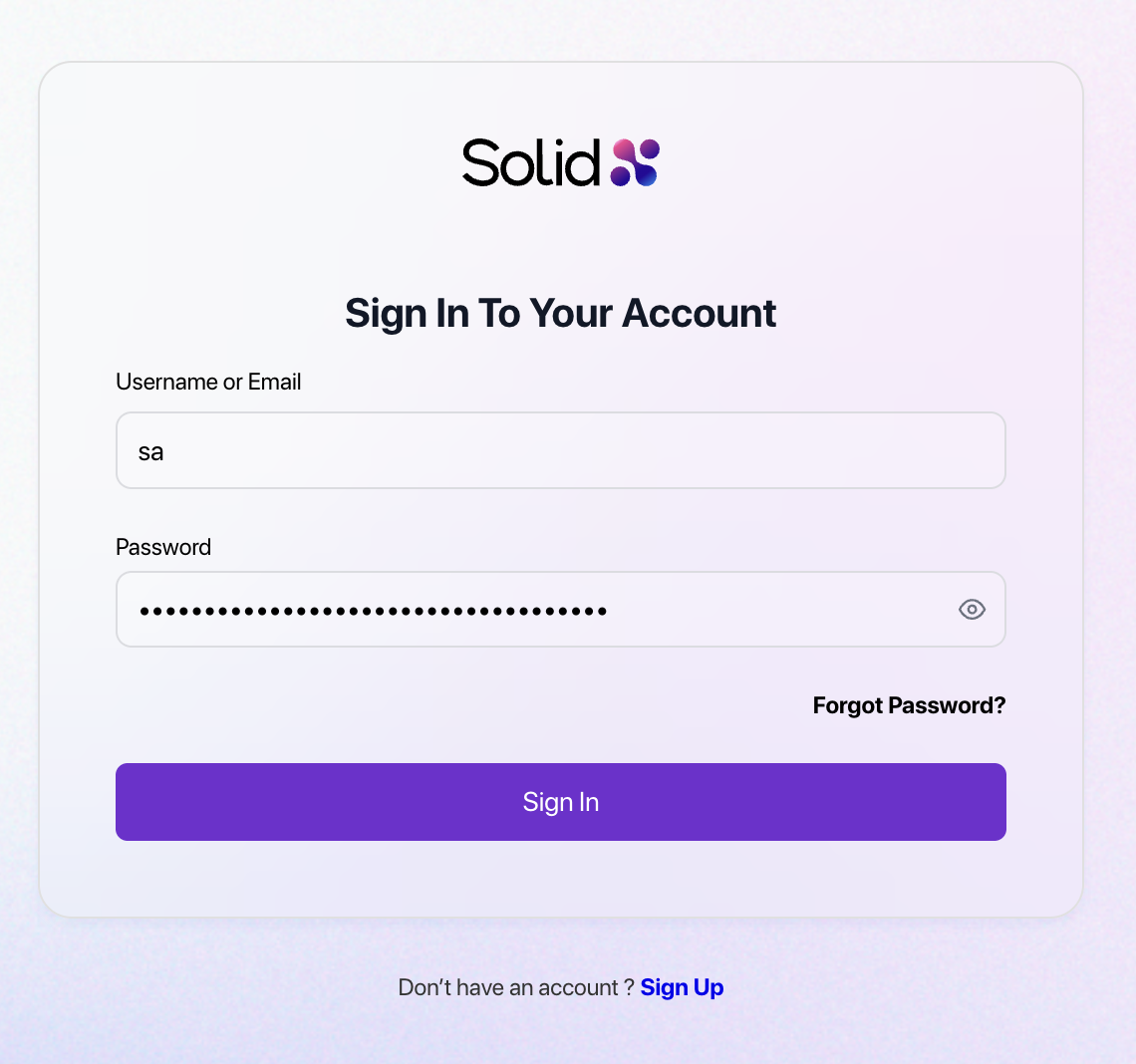
Log In as Super Admin
Use the credentials displayed after seeding to access the admin panel with full permissions.
After logging in, you will be redirected to the default landing page of the admin panel. If no landing page is configured, you will see the default landing page as shown below.

Setup Complete - Ready to Build!
Your SolidX environment is now configured and the admin panel is accessible.
You're ready to build a fully functional school fees portal application using the SolidX App Builder. No coding required—just visual configuration to create entities, relationships, workflows, and business logic.
Let's start building!